Business Process Reengineering with Examples: Successful Case Studies
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is about reshaping business paths to lead to big improvements. It's like rebuilding a car design so it can move more swiftly, last longer, and give a smoother ride. BPR isn't just changing a tire; it's rethinking the whole vehicle design for better trips. Considering performance metrics like cost cut down percentages, customer satisfaction ratings, and increase in work output, help us measure how our new model is running. Done right, it can turn an old clunker into a race car. Now buckle up, and let's speed into learning this fascinating process.
One example of business process reengineering is the transformation of manual paper-based invoicing to an automated electronic invoicing system. This involves redesigning the invoicing process to improve speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness while reducing the dependency on physical paperwork.
Business Process Reengineering Definition
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is a strategic approach used by organizations to completely rethink and redesign their existing business processes for significant improvements in areas such as cost, quality, service, and speed.
The key aspect of BPR is that it's not about making small improvements - it's about
radically overhauling the existing processes. This is vital because incremental changes often do not result in the dramatic enhancements necessary to stay competitive in today's fast-paced business environment.
To simplify, picture your business processes as a machine. Business process reengineering is like disassembling the machine entirely and rebuilding it from scratch. This ensures that every part of the machine is not just polished or adjusted, but rethought and designed for maximum efficiency and productivity.
Business Process Reengineering
The goal of BPR is to identify and eliminate non-value-adding activities within the organization's processes, thereby creating a leaner, faster, and more efficient system. It involves rethinking how work is done, using technology to enable that rethinking, and improving the organization's core business processes.
More than just focusing on isolated tasks or specific departments, BPR takes a holistic approach by considering end-to-end processes. This means looking at how each department or function connects with one another to create a streamlined and integrated workflow.
For instance, instead of just tweaking the customer service department to handle complaints more efficiently, BPR might involve restructuring the entire customer journey to make it more seamless from order to delivery, ultimately enhancing the overall customer experience.
Understanding the fundamental concept of BPR is essential before exploring successful case studies and implementation strategies as it lays the foundation for comprehending the depth of organizational change that occurs during this process.
Now equipped with the understanding of Business Process Reengineering (BPR), we can investigate successful case studies and implementation strategies that have revolutionized various industries.
Measuring Success with Performance Metrics
The implementation of business process reengineering is a significant investment for any organization. To ensure that this investment is paying off, it's crucial to establish and track key performance metrics. These metrics serve as the yardstick against which progress and success are measured, providing actionable insights into the impact of the reengineered processes.
When it comes to measuring success with performance metrics, there are several key areas that organizations focus on:
Cost Reduction Percentages
Cost reduction is a common objective of business process reengineering. By streamlining processes and eliminating redundancy, organizations aim to reduce operational costs significantly. Tracking the percentage reduction in costs provides clear visibility into the financial impact of the reengineering efforts. For example, a 20% reduction in operational costs directly reflects the efficiency gained through the reengineered processes.
Cycle Time Improvements
Efficiency gains can also be measured through improvements in cycle time. This metric focuses on the time taken to complete a specific task or process. A 40% decrease in process cycle time indicates the enhanced speed and agility achieved through reengineered workflows.
Customer Satisfaction Ratings
The ultimate goal of business process reengineering is to deliver improved value to customers. Monitoring customer satisfaction ratings before and after BPR implementation provides insight into the impact on service quality. A 15% increase in customer satisfaction scores reflects the positive influence of reengineered processes on customer experience.
Increase in Productivity
Productivity metrics play a pivotal role in assessing the overall impact of reengineering efforts on organizational output. An increase in productivity after BPR implementation, such as a 30% rise in productivity levels, demonstrates the effectiveness of optimized workflows and resource allocation.
It's important for organizations to select and utilize relevant performance metrics that align with their strategic objectives and the specific outcomes they aim to achieve through business process reengineering. The choice of metrics should be driven by the desired impact of the reengineering efforts and should offer actionable insights that facilitate data-driven decision-making.
By leveraging these performance metrics, organizations gain valuable visibility into the tangible results of their business process reengineering initiatives. Real-time monitoring and analysis of these metrics enable continuous improvement and fine-tuning of reengineered processes, contributing to sustained success and long-term competitiveness in today's dynamic business landscape.
Now that we've explored how performance metrics play a crucial role in measuring the success of business process reengineering, it's essential to understand how these insights drive further innovation and improvement strategies.
Six Sigma vs Business Process Reengineering (BPR) - A Comparison
What is Business Process Reengineering (BPR)?
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is process of streamlining the processes by challenging the each step of the current process. The classic example of BPR is from the banking industry. In the late 1980’s and late 1990’s, if we wanted to withdraw money from our bank account, following steps were involved:
- Go to the bank during banking operation hours
- Fill in the withdrawal requisition slip
- Submit the slip and receive a token number
- Wait until our token number is announced by the Cash Teller
- Then receive the money
The above process had a lot of drawbacks. We could go to the bank only during their operational hours. Certain banks did not have many branches and thus, we had to go to the location of the bank. We had to fill the withdrawal requisition slip. We had to wait in a queue where others are also waiting to withdraw money and so on.
What did the banking industry do? They radically changed the entire process and in the early 2000’s got in the ATM machines. Do we now need to go to our banks? Do we have to wait in queues? Do we need to fill any withdrawal slips? Everything’s changed. This kind of a process improvement is called as Business Process Reengineering.
In contrast to BPR, Six Sigma is an approach which focuses on variation (or uncertainty) reduction in processes. It is the only methodology available which is a documented process improvement methodology. Unlike BPR, Six Sigma uses a five step method to identify root causes and provide world-class solutions. Six Sigma does not involve a complete overhaul of the process like BPR. However, it requires out-of-the-box thinking and questioning status-quo to identify and implement solutions.
An example of a banking process will be as follows. Consider that you are applying for an account opening process in a bank. You will need to go through the following steps:
- Meet the banks representative and fill out Account Opening Form
- Provide KYC (Know Your Customer) details and submit identification proofs
- Telephonic verification takes place
- Physical Home Address verification takes place
- Account is created and check book and ATM card is sent to customer address
The above process may have an Account Opening timeline target of 48 hours and the mean performance of the process may be 40 hours, however, the variation may be as high as 8 days. There may be multiple instances where the account opening took place as late as 8 days. That’s a long time which is good enough to have angry customer!. And the customer does not look at the mean performance but looks at this specific variation just happened to him.
When a Six Sigma project is applied to above process, it focuses on reducing this variation and streamlining the processes to achieve customer satisfaction. It may not necessarily change the entire process flow like it takes place in BPR. This is the key difference between Six Sigma and BPR.
Below is a brief comparison of BPR and Six Sigma:
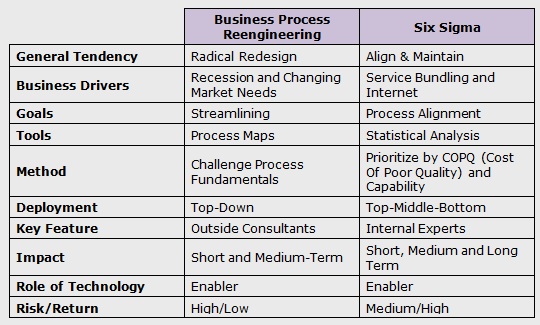
Six Sigma vs Business Process Reengineering - A Comparison
Enhancing Customer Relations through BPR
When a company decides to reengineer its processes, the primary goal is often to make things work better and more efficiently. From manufacturing to customer service, each area has the potential to be transformed for the better. However, when it comes to enhancing customer relations, this kind of change can be of tremendous value.
Improving Service Quality
Traditional waiting times and delays don't sit well with modern consumers. By reengineering business processes, companies can reduce customer query resolution time, leading to improved satisfaction among customers. This could mean streamlining call center operations or implementing self-service options that expedite issue resolution. Efficiently handling customer inquiries not only saves time for your customers but also allows your employees to focus on providing a higher level of service rather than getting bogged down in administrative tasks. It's a win-win situation that directly enhances the overall customer experience.
Streamlining Processes
By cutting down on unnecessary steps and simplifying complicated procedures, businesses can make the journey from inquiry to solution smoother and more seamless. For example, an e-commerce company may streamline its order processing and delivery tracking systems, ensuring that customers receive accurate and timely information about their purchases. This reduces frustration and instills confidence in the company's reliability. Streamlining processes doesn't just make life easier for customers; it also optimizes internal workflows, allowing employees to handle tasks more efficiently which benefits both the company and its valued customers.
By focusing on BPR from a customer relations perspective, companies can identify pain points in their current processes and create solutions that directly address customer needs.
Some might argue that such large-scale changes are risky and might alienate loyal customers who are used to the old way of doing things. However, research shows that when reengineering efforts are well-executed and aligned with customer needs, they result in increased satisfaction and loyalty in the long term.
For instance, a telecommunications company conducting business process reengineering successfully reduced its response time for billing inquiries. This led to a significant increase in customer satisfaction scores and a noticeable decrease in the number of customer complaints filed.
By aligning processes with the needs and expectations of their patrons, businesses can establish strong relationships with their customers while simultaneously improving their operational efficiency.
In essence, understanding how business process reengineering positively impacts customer relations is pivotal in comprehending the core steps necessary for successful BPR implementation.
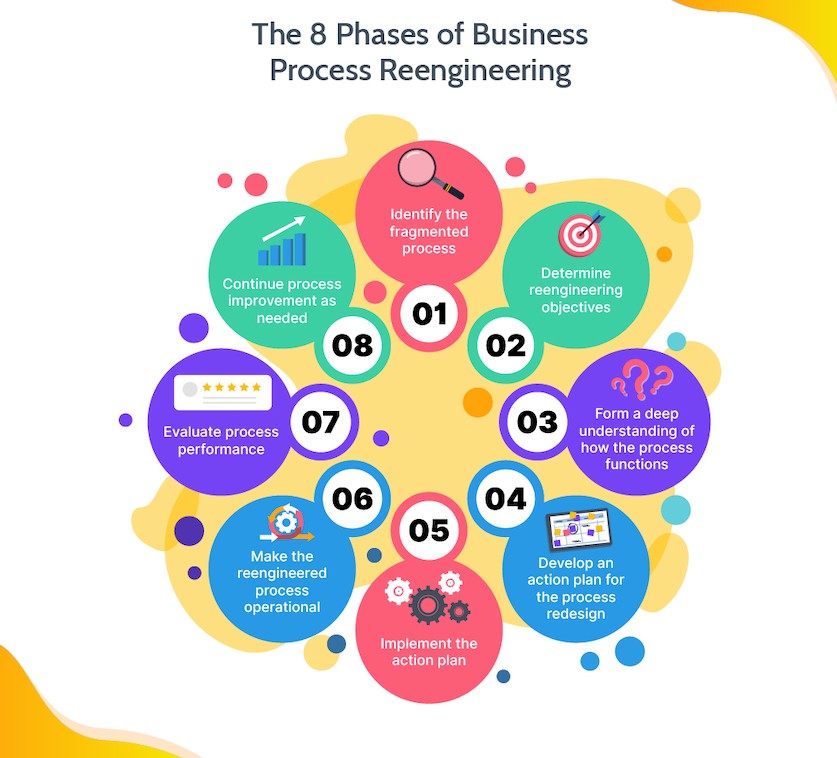
Core Steps for Successful BPR
Business process reengineering (BPR) involves a series of strategic and methodical steps aimed at overhauling and improving operational workflows. Each step is instrumental in ensuring the success of the entire reengineering process. Let's explore these critical steps in detail.
Step I - Identifying Processes for Redesign
The first phase of BPR involves analyzing existing processes to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. This often requires input from various teams and extensive data collection. By examining each stage of the process, you can pinpoint bottlenecks, redundancies, and areas that slow down productivity or increase costs. The goal is to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and ultimately improve customer satisfaction.
Step II - Redesigning Processes
Once the inefficiencies have been identified, it's time to formulate a new process blueprint that incorporates innovative technologies and best practices to address the issues identified during the analysis phase. Cross-functional collaboration is key, as various departments need to work together to ensure that the redesigned processes align with overall organizational goals and objectives.
Moreover, this step involves leveraging advanced technologies such as automation, artificial intelligence, or data analytics to further streamline operations, significantly improving the efficiency and effectiveness of the newly designed processes.
Step III - Change Management
Implementing new processes isn't just about introducing change; it's about managing that change effectively. Smooth transition hinges on providing comprehensive training and support to employees who will be working with these new processes. Embracing change can be challenging, so clear communication about the reasons behind the changes and demonstrating the benefits they will bring is crucial. Change management ensures that all employees are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to adapt to the revamped processes seamlessly.
A successful BPR also considers ongoing support mechanisms, continuous feedback loops, and performance evaluations to gauge the effectiveness of the implemented changes.
Remember, effective change management is not just about informing people what will be different—it's about consistently communicating why it needs to be different.
Mastering these core steps for successful BPR implementation lays the foundation for unlocking new levels of efficiency, agility, and competitive advantage within an organization.
Having mastered these core steps for successful BPR implementation, let's now navigate through strategies to overcome challenges that may arise.
Overcoming BPR Challenges
Implementing Business Process Reengineering (BPR) may sound promising on paper, but in reality, it comes with its share of challenges. Change is hard for many people--it's natural to feel a little uneasy about new things, especially when it might affect your day-to-day work life. Employees might resist changing how they've always done things, even if the change is for the better or brings more efficiency to their role.
Moreover, capturing and documenting existing processes can be a daunting task. Often, processes are spread across different departments and individuals, making it difficult to create a comprehensive picture of all the interconnected processes within an organization. Without clear and accurate documentation, it becomes complicated to identify areas that need improvement.
Consider a company trying to reengineer its supply chain processes. The existing information might be scattered across multiple systems and teams, making it laborious to piece together a holistic understanding of how things currently operate. This lack of visibility hinders the ability to reimagine and redesign these processes effectively.
But these challenges shouldn't deter you from pursuing BPR. Instead, identifying these potential stumbling blocks allows us to build strategies to overcome them.
To tackle resistance to change, providing ample training opportunities and involving employees in the decision-making process can significantly mitigate apprehensions. When individuals feel included in the transformation journey and understand why changes are necessary, they are more likely to embrace the new processes.
As for grappling with documentation complexities, leveraging technology such as process mapping software can streamline this endeavor. Through such tools, organizations can visualize their existing processes more comprehensively and identify redundancies or inefficiencies more effectively.
For instance, using process mining software aids in reconstructing actual business processes from digital traces in enterprise databases. This not only helps in creating accurate documentation but also provides insights into how processes are executed in real life, allowing for more precise identification of bottlenecks and wasteful steps.
By acknowledging these challenges and proactively implementing strategies to tackle them head-on, organizations can harness the full potential of BPR without being burdened by roadblocks along the way.
In navigating the intricate landscape of BPR challenges and solutions, it's crucial to examine practical case studies that exemplify successful implementation. One such noteworthy exploration awaits us with IBM's triumphant journey in BPR success.
BPR Success: IBM's Case Study (Business Process Reengineering Example)
IBM, a titan in tech and innovation, implemented Business Process Reengineering to revamp its ordering and delivery processes successfully. By overhauling their traditional methods, IBM achieved a remarkable reduction in both ordering and delivery times. This meticulous transformation not only elevated their operational efficiency but also led to substantial cost savings—a key indicator of successful BPR implementation.
One of the pivotal shifts within IBM’s reengineering strategy was the introduction of advanced technologies to streamline their ordering and delivery processes. This integration allowed for more seamless communication across various functions, facilitating a synchronized flow of information. Consequently, the optimization of these workflows resulted in marked improvements in order processing times and accelerated product delivery.
Moreover, the implementation of BPR at IBM catalyzed a shift towards a more customer-centric approach. By aligning their processes with customer needs and market demands, the organization was able to enhance its service delivery capabilities, ultimately improving customer satisfaction. This strategic realignment not only boosted customer loyalty but also broadened IBM’s competitive edge in the industry.
Consider this: A customer orders a product from IBM and experiences a significantly reduced waiting period for delivery, thanks to the expedited processes facilitated by BPR. This enhanced customer experience not only fosters goodwill but also strengthens the likelihood of repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
It’s clear that IBM’s successful embrace of BPR didn’t just optimize internal operations; it also established a strong foundation for sustainable growth and profitability. This exemplary case serves as a testament to the transformative power of strategic reengineering when executed with precision and foresight.
The success story demonstrated by IBM illustrates how deliberate process reengineering can yield profound enhancements not only within an organization's internal operations but also across its broader value chain and customer experience.
Now, let's delve into the triumph of Ford Motor's strategy in navigating through the complexities of Business Process Reengineering.
BPR Triumph: Ford Motor's Strategy
Now, let's take a closer look at how Ford Motor Company utilized Business Process Reengineering (BPR) to transform its operations and gain a competitive edge. Ford's foray into BPR resulted in substantial improvements across their production processes and supply chain management, pivotal in elevating product quality while achieving cost savings. The intricate details behind Ford's BPR triumph can provide valuable insights into the successful implementation of reengineering strategies within large-scale organizations.
Ford Motor Company's BPR initiative aimed to streamline various operational facets, including manufacturing, logistics, and distribution. By identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks within these areas, Ford implemented strategic changes that led to far-reaching improvements. For instance, reconfiguring production layout, optimizing assembly line processes, and enhancing inventory management were instrumental in maximizing efficiency and reducing waste, resulting in significant reductions in production costs and turnaround times.
Furthermore, Ford's emphasis on revamping supply chain management through BPR led to enhanced coordination with suppliers, improved inventory visibility, and streamlined delivery processes. These enhancements not only facilitated seamless production operations but also fostered stronger relationships with suppliers, ultimately contributing to increased agility in responding to market demands.
For example, by analyzing demand patterns and aligning them with production schedules, Ford was able to minimize inventory holding costs and effectively manage stock levels, ensuring a consistent supply of materials while minimizing excess inventory.
Unveiling the key strategies that drove this success is essential in understanding how BPR can be effectively harnessed to drive transformational change within an organization. From overhauling production systems to optimizing supply chain operations, each element played a crucial role in propelling Ford Motor Company to new heights of operational excellence.
By dissecting the specific strategies employed by Ford Motor Company and their resulting outcomes, we gain valuable insights into the tangible benefits that can be achieved through comprehensive Business Process Reengineering initiatives. Let's explore these strategies in detail and understand the transformative impact they had on Ford's business landscape.
The case of Ford Motor Company underscores the transformative power of Business Process Reengineering (BPR) when executed strategically. These insights from real-world examples serve as guiding beacons for organizations aiming to revitalize their operational frameworks for enduring success.
What is the definition of business process reengineering?
Answer: Business process reengineering is the fundamental restructuring and redesign of business processes to achieve substantial improvements in performance, quality, and efficiency. It entails analyzing and rethinking existing processes from scratch, rather than making incremental changes. According to a study by Harvard Business Review, companies that applied business process reengineering achieved an average cost reduction of 18% and a time reduction of 35%.
What are some common challenges or pitfalls to avoid when implementing business process reengineering?
Answer: Some common challenges or pitfalls to avoid when implementing business process reengineering include resistance to change, lack of communication and collaboration among stakeholders, inadequate support from top management, and unrealistic expectations. Research shows that 70% of reengineering efforts fail due to lack of employee engagement and buy-in, while 50% fail because of poor planning and execution. Therefore, it is essential to address these challenges by involving employees throughout the process, providing clear communication channels, garnering top-level commitment, and setting realistic goals and timelines.
Can you provide real-life case studies or success stories of companies that have implemented business process reengineering?
Answer: Certainly! One real-life success story of business process reengineering is IBM. By implementing reengineering strategies, IBM was able to streamline their global procurement process and reduce lead time from 40 days to just four days, resulting in cost savings of $1 billion annually. Another successful case is Ford Motor Company, where the implementation of process reengineering led to a reduction in order-to-delivery time by 75%, resulting in increased customer satisfaction and improved profitability. These examples highlight the effectiveness of business process reengineering in improving efficiency and achieving significant cost savings for companies.
How can business process reengineering improve efficiency and productivity?
Answer: Business process reengineering (BPR) can significantly improve efficiency and productivity by redesigning and streamlining processes, eliminating unnecessary steps, and implementing technological advancements. By analyzing and reorganizing workflows, BPR optimizes resource utilization, reduces costs, and enhances productivity. For instance, a study conducted by McKinsey found that companies implementing BPR achieved 30% to 50% cost reductions while improving cycle times by 50% to 75%. BPR enables organizations to adapt to changing market conditions, enhance customer satisfaction, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving business landscape.
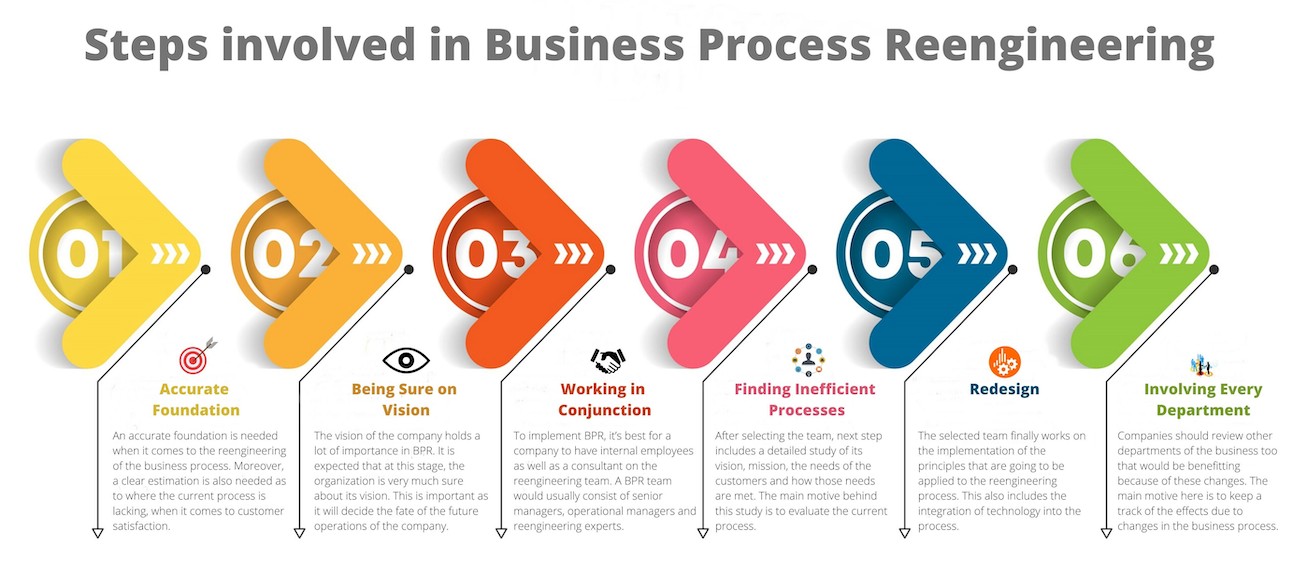
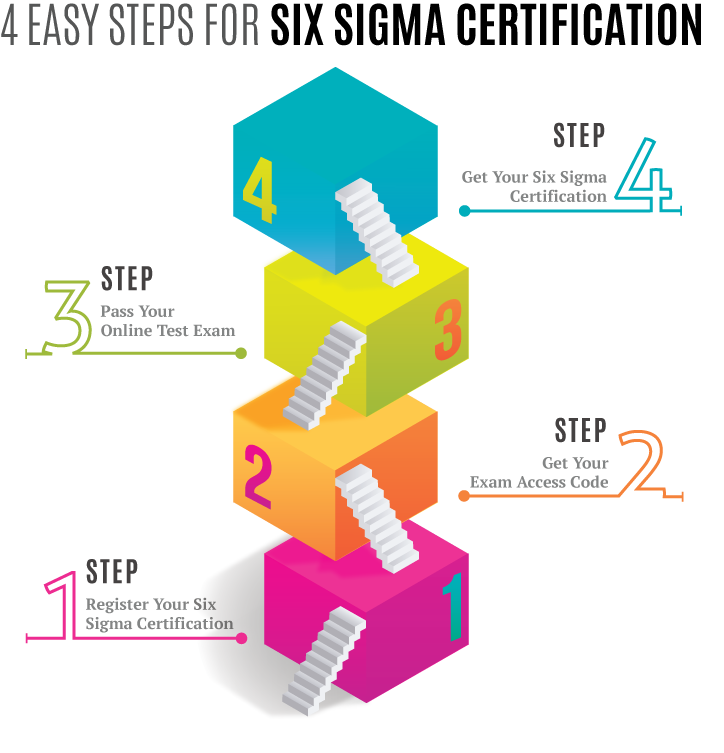
Business Process Reengineering Steps
Are there any specific industries or types of businesses that can benefit most from business process reengineering?
Answer: Yes, there are specific industries and types of businesses that can benefit greatly from business process reengineering. Industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, financial services, and customer service-oriented businesses can see significant improvements in efficiency, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction through the redesign of their processes. For instance, a study by McKinsey found that companies in the manufacturing sector achieved an average 20-30% improvement in productivity after implementing business process reengineering. Similarly, healthcare organizations have witnessed benefits like reduced wait times and improved patient experience by reengineering their processes.
What is the difference between Lean and Six Sigma?
Answer: The distinction between Lean and Six Sigma lies in their unique approaches to problem-solving within a business context. Lean primarily focuses on identifying and eliminating waste in processes, employing strategies to streamline operations and enhance efficiency. It emphasizes teamwork and encourages continuous improvement to address problems related to unnecessary steps or resources. On the other hand, Six Sigma centers around reducing variations and defects in processes, relying on statistical methods and data-driven analysis to achieve consistent, high-quality outcomes. Both methodologies employ KPIs to measure success, ensuring that improvements align with overall business objectives.
In essence, combining Lean and Six Sigma provides a powerful way to address problems comprehensively. A strategic plan that integrates the strengths of both methodologies, utilizing the expertise of a cross-functional team, can result in more effective solutions to complex business challenges. While Lean focuses on optimizing processes, Six Sigma adds precision and statistical rigor, creating a balanced approach that enhances the overall efficiency and quality of products or services. Successfully implementing these methodologies requires a well-thought-out plan and collaboration among experts to avoid the potential failure of improvement initiatives.
Recap for Business Process Reengineering with Examples
Business Process Reengineering (BPR) is a transformative approach aimed at overhauling and optimizing company processes for enhanced efficiency and performance. Throughout successful case studies, it's evident that BPR goes beyond merely fine-tuning existing workflows; it involves a radical redesign to achieve significant improvements in productivity, cost-effectiveness, and overall organizational success. Notable examples showcase how BPR can lead to streamlined business process management, enabling companies to adapt to evolving market demands and gain a competitive edge.
One crucial aspect illuminated by these case studies is the role of leadership in driving and sustaining the BPR initiatives. Effective leadership is instrumental in fostering a culture of innovation and change, ensuring that the entire organization is aligned with the reengineered processes. Employee satisfaction emerges as a key metric influenced by BPR, as the restructuring efforts aim not only for operational efficiency but also for creating a workplace environment that empowers and motivates employees. By adopting successful BPR strategies, companies can witness improvements in their business process management, creating a positive ripple effect throughout the organization, from enhanced employee satisfaction to increased overall productivity.
To delve deeper into strategic methodologies that complement Business Process Reengineering, we encourage you to download our free Six Sigma Framework book. This resource provides valuable insights into process optimization, aligning seamlessly with BPR initiatives. Written to assist businesses in navigating through complex company processes, the Six Sigma Framework book is an invaluable tool for those aiming to achieve lasting success in their continuous improvement endeavors.
 SIXSIGMA INSTITUTE™
SIXSIGMA INSTITUTE™